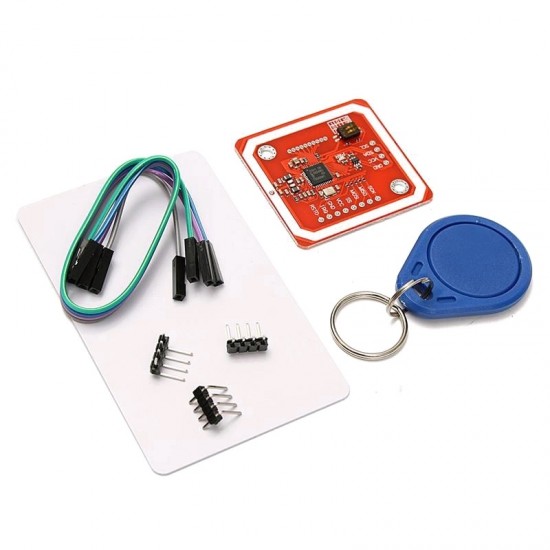
- Stock: Out Of Stock
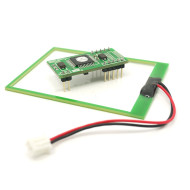
- Model: PN532 NFC RFID Module
- SKU: 3736
We recently hear a lot about NFC. This feature is available in the latest high end smart phones present in the market. NFC stands for Near Field Communication. NFC is a protocol designed for smart phones and similar devices to establish radio communication with each other by touching them together or bringing them into close proximity, usually no more than a few centimeters. This type of communication is needed for simple and fast data exchange between devices.
And for engineers and hobbyists, it is another important communication method. And for establishing this NFC communication, we can use this PN532 MODULE. This module acts a modem to send and receive data.
PN532 is NFC RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) module. This module is built around NXP PN532 IC. NXP PN532 IC is very popular in NFC applications.
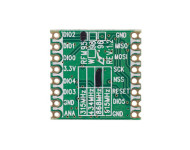
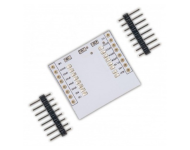
PN532 NFC Pinout Configuration
The description of each pin of the module is given below.
Pin Number | Description |
VCC | Should be power source. |
GND | Should be connected to ground. |
SDA/TXD | SDA: Serial Data pin[I2C Interface] TXD: Transmit pin[UART Interface] |
SCL/RXD | SCL: Serial Clock pin[I2C Interface] RXD: Receive pin [UART Interface] |
SCK | Serial Clock pin [SPI Interface] |
MISO | Master Input Slave Output pin [SPI Interface] |
MOSI | Master Output Slave Input pin [SPI Interface] |
SS | Slave Select pin [SPI Interface] |
IRQ | Interrupt Signal pin [SPI Interface] |
RSTO | Reset pin |
PN532 NFC Module Features and Specifications
- 80C51 microcontroller core with 40 Kbyte ROM and 1 Kbyte RAM
- Highly integrated analog circuitry to demodulate and decode responses
- Buffered output drivers to connect an antenna with minimum number of external components
- Integrated RF level detector
- Integrated data mode detector
- RFID reader/writer mode support [MIFARE 1k, 4k, Ultra light, and DESFIRE cards, ISO/IEC 14443-4 cards such as CD97BX, CD light, DESFIRE, P5CN072 (SMX), INNOVISION Jewel cards such as IRT5001 card, FELICA cards such as RCS_860 and RCS_854]
- Built in PCB Antenna, with 5cm to7cm communication distance
- Supports MIFIRE higher transfer speed communication at 212Kbits/s and 424 Kbits/s
- Supported host communication: SPI Interface, I2C Interface and High Speed Serial UART
- Flexible interrupt using IRQ pin
- Hard reset with low power function
- Power down mode per embedded firmware
- Automatic wake up on HSU,I2C and SPI interfaces when device is in power down mode
- Programmable timer
- Contactless communication at 13.56MHz
- On-board level shifter, Standard 5V TTL for I2C and UART, 3.3V TTL SPI
- Work as RFID reader and writer
- Work as RFID card or a virtual card
- Operating voltage: +2.7V to +5.5V
- On-board level shifter: Standard 5V TTL for I2C and UART, 3.3V TTL SPI
- Low power modes: Hard-Power-Down mode (1µA typical), Soft-Power-Down mode (22µA typical)
- Operating temperature: -30ºC to +85ºC
Note: Complete technical details can be found in the PN532 Datasheet given at the bottom of this page.
Similar RFID Reader Modules
RMD6300, RC522, EM-18
Where to use PN532 NFC Module?
- PN532 module basically used to setup a communication mode to devices for quick data exchange.
- PN532 module can be used on experimental products to communicate with smart phones and PC.
- The module is used as a communication shield for ARDUINO and PI platforms.
- The module can be used an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) reader and writer.
- The module itself can be used as RFID card.
- The module consumes very less power so it can be used in mobile systems which work on battery.
- The module can be used on any controller (or processer) who has any one of three Interfaces (I2C, UART, and SPI).
How to use PN532 NFC Module?
For using PN532 module, first we will choose the mode of communication between MODULE and CONTROLLER. As mentioned earlier, this module has three interfaces, of which we have to choose one. Remember at any given point of time only one of three interfaces can be used. All three cannot be used together. We will have to choose the mode of interface using two switches solder to the board. The switches are S1 and S2 shown in pin diagram.
S1 | S2 | Interface |
OFF | OFF | HSU (High Speed UART) |
ON | OFF | I2C |
ON | ON | SPI |
Choose the mode of interface and corresponding state of switches from above table. Next toggle the switches S1 and S2 to those positions.
After choosing the type of interface, connect the module to the controller or processor. Say if you opted to use I2C, then connect module to I2C of the controller. If you opted to use SPI, then connect module to SPI of controller.
After interfacing you have to download the library files for the module from corresponding websites. Say for ARDUINO platform [https://www.arduinolibraries.info/libraries/adafruit-pn532]. Save the library files in the IDE program files.
Now all that left is to write the program for the controller or ARDUINO in the IDE software. And do call up on the saved library files while writing the program. With those libraries we can directly communicate with the module while skipping all the steps of communication protocol.
Once the programming is done, power up the circuit to get the desired response.
Applications
- Media or Data sharing
- Robotics
- Smart Phones and Smart devices
- Security systems
- Computer Peripherals
- Package Identification
- Theft protection systems

































































































-190x150h.jpg)